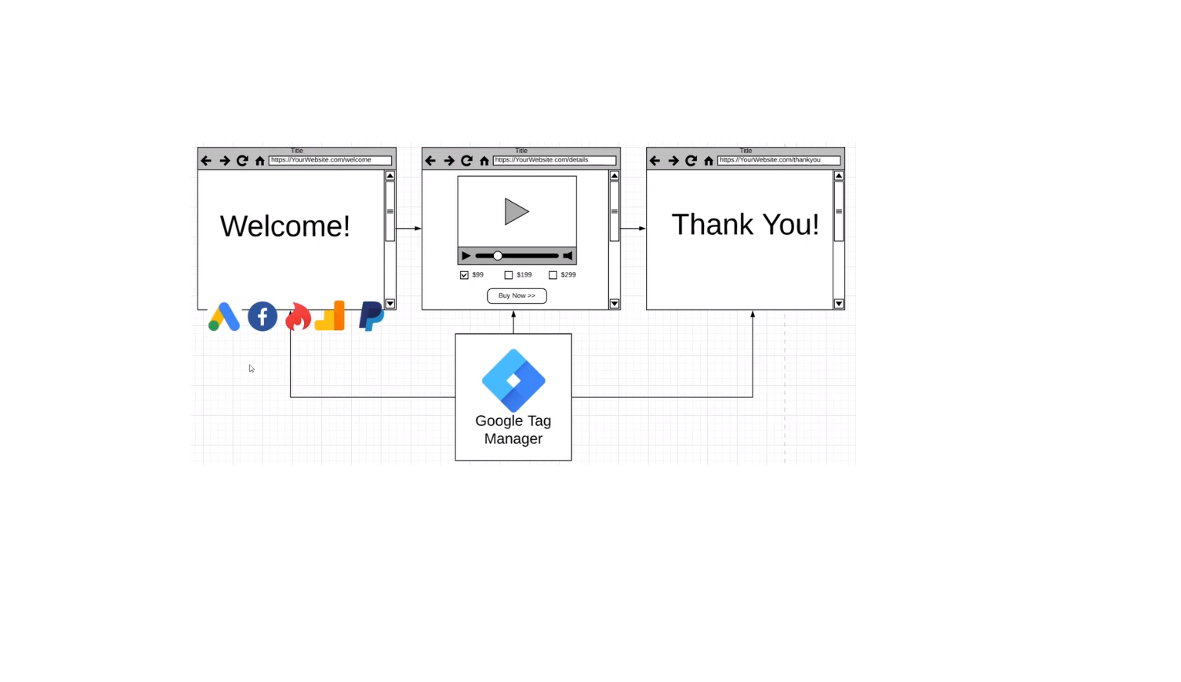
What tag managers are?
A tag management system helps you to get greater visibility of what´s happening on a specific page of your website and reports additional details. These additional details are something you can send directly to your Google Analytics Account for instance or any 3rd party app.
At the same time, you can train Google Tag Manager for retargeting purposes other social media platforms. An example would be when you install Facebook or Paypal pixels to track the number of visitors coming to your website from these platforms. In a nutshell, GTM is a control panel that is fired by defined actions that happen on your page.
Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics
GA by itself only collects the data, stores information and builds reports. GA, unfortunately, does not offer a lot of information about specific details regarding visitors behaviour. For that reason, we add GTM to collect data and send it to Google Analytics or other applications to build reports or store the information.
Analytics does not have a lot of visibility about specific details about visitors behaviour. We remove instead and add GTM to collect data and send it to GA or third-party apps to build reports or store the information.
Installing Google Tag Manager
When installing GTM on your website there are 2 scripts you need to install. One script goes in the head of your website´s code and the 2nd script goes into the body. This will work for instance if you need to also implement ads pixels.
If you are using a WordPress built website there are three options you have to install GTM:
- Edit the theme settings using a Divi builder or any other builder
- Edit the theme via the theme editor
- or Install a plugin
GTM Tags
The way google tag manager works is by defining tags that communicate with other applications about what is happening on the website. There are 2 types of tags you can use:
- Google built-in tags for common queries
- Custom HTML tags you can define according to your needs
GTM Triggers
With triggers, you can track when a pageview happens you tell GTM to fire specific ads for example.
When someone clicks on a specific video you can trigger certain apps to send information to. When someone is playing a video you can send that information to Google analytics or a platform of your choice. As you can see triggers can send information to different platforms and at different times as well.
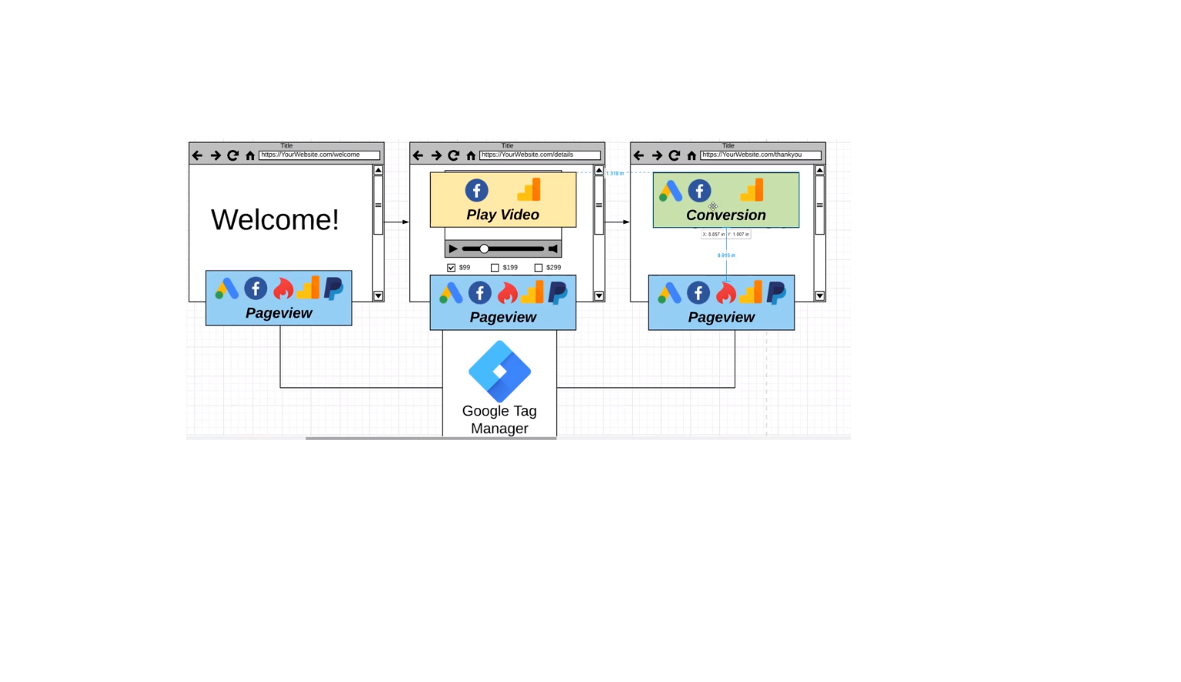
- page view trigger (when the page is loading)
- click triggers (hyperlinks)
- user engagement (they are for instance used when a video is watched)
- other types of triggers
GTM Variables
A variable is an information that GTM needs to do a specific job. A variable provides information that an admin needs to analyze certain aspects of the behaviour of a website. We can define it as a page path, a certain video or the value of the conversion rate. Platforms have now more information to analyze by defining variables. You can have more variables defined for each information you are collecting making it easier for you to organize information.
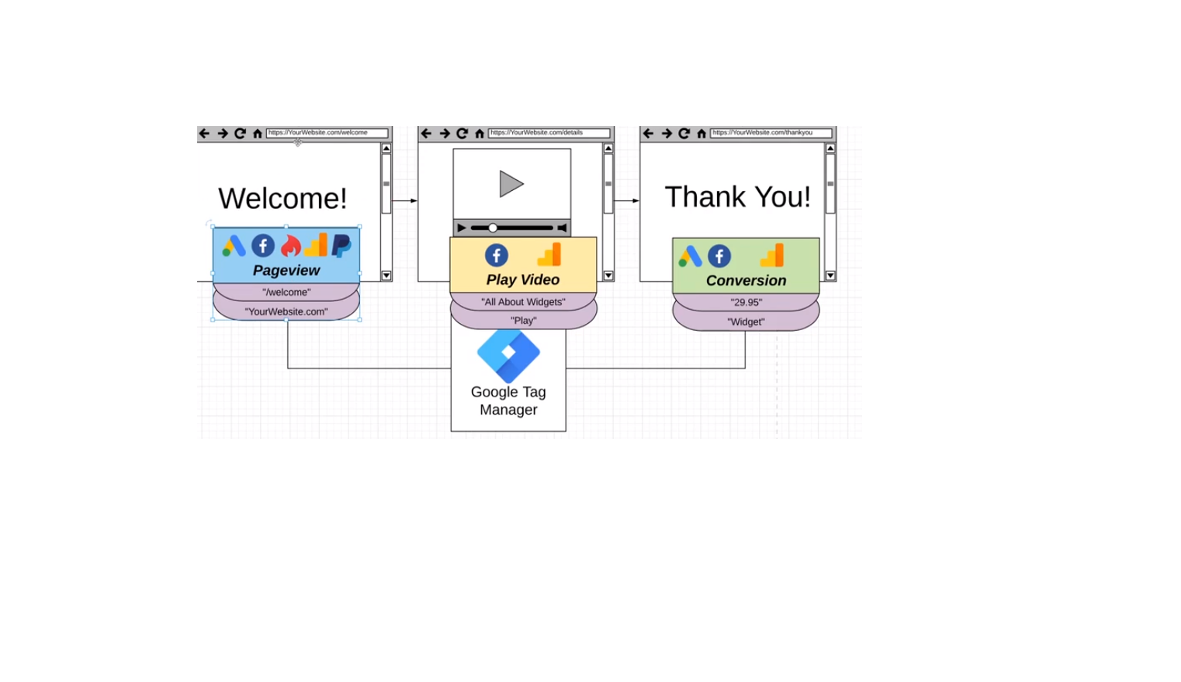
- Built in variables that can be standard and pre-configured variables.
- User defined variables that are custom variables you can create.
GTM Data Layer
A data layer is a place where you can temporarily store details important to tag manager before it gets to GTM. There are 2 parts to a data layer: the first one is the key and the second is the value of the key. The value of the key can change but not the key.
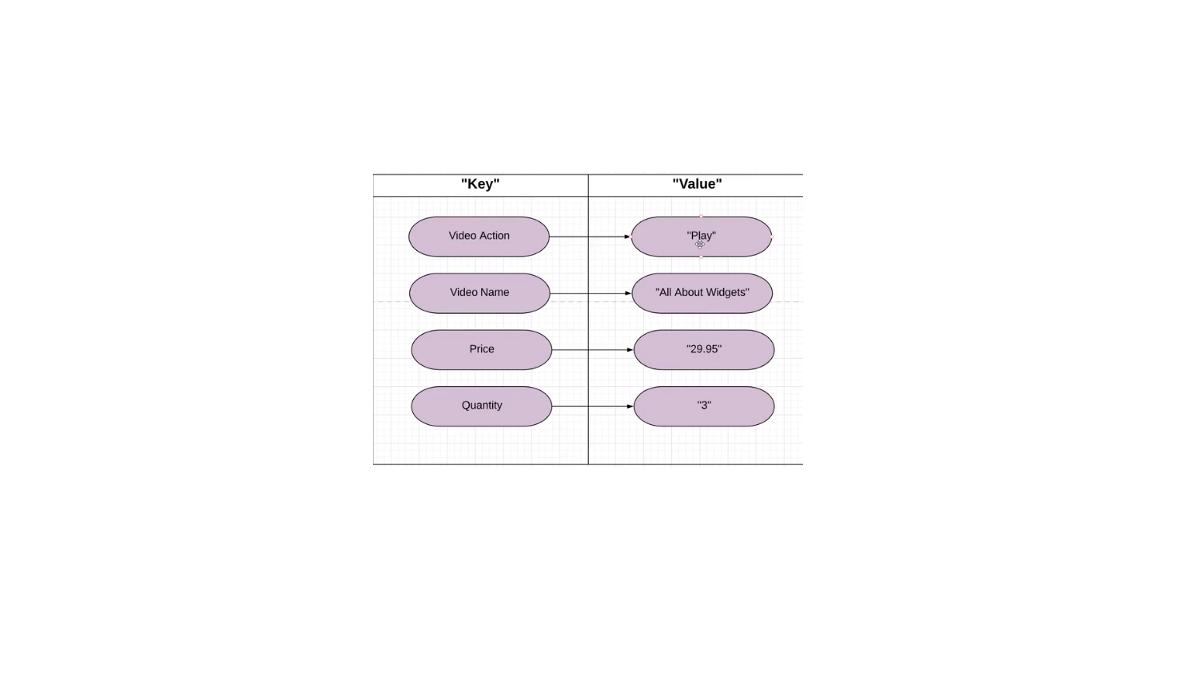
Every time a page loads when GTM loads it creates a data layer. The key is the one the next page loads a new data layer gets built. In tag manager, you can see your own data layer as in the example below. When you change the page new values are being generated:
We can send this data to GA or Facebook for analysis. You need to define what type of information you can track.
GTM organization
The way GTM is organized is by using an account and a container type of structure. The structure usually starts at a user level and the administrator of the account is the one giving permissions to access the account. What happens is that companies deal with multiple vendors and the access to that account is given to multiple admins. This can create problems, especially if when changing the vendor his/her access is not removed. For that reason, you want to make sure you add your vendors or employees as users of the account only.
When setting up your GTM you should take into account:
Naming structures
Tag Manager and Google Analytics sort things alphabetically which helps to better understand the hierarchy of the information. But you should also define your own conventions to make sure everyone on your team has clear guidelines about how to set up extra tags, variables or data layers.
A company needs to define a naming convention to be shared with all team members and avoid duplicates. The same happens with triggers, variables and data layers there is a hierarchy defined as well to optimize the information and avoid problems.
Folders
You can create folders inside GTM for each group of tags, variables or data layers to store all the information together. Similar to the PC folders you want to keep all the information organized. You can also have folders by the vendor you can focus and organize things by each vendor.
GTM in preview mode
Preview is a way to make sure all the changes made in GTM are done and you can test them. This is just for you to see your changes. It shows what places change and where and you can test it before you push those changes live. The preview gives you the container name to see if it matches with the one you have previously defined.
GTM Workflow
You can set up a workspace when you have multiple people involved in a project. And undo errors or mistakes and also to allow more than one user work in the workspace. In the overview, you can see all the changes and that is associated with multiple users given access to the workspace.
Once you set up everything, you preview and test and once you are happy you can publish those changes and they will become versions.
You can create a new container for further modifications and see them as unmerged versions and verify before publishing.